30 years of achievements
Timeline
First computer, first LAN and autonomous internet domain
February 1991. CRS4 gets its first computer. It is an Apple Macintosh IIfx, which is connected via telephone line and a 4.8 Kbit/s modem with the Cagliari section of the INFN, the National Institute for Nuclear Physics, thanks to the hospitality of its director Sergio Serci and his collaborators, Alberto..Read More
First recruitments to CRS4
The first researchers were hired, with direct call, from CERN (Pietro Zanarini), the University of Chicago (Gianluigi Zanetti), Princeton (Kanthan Pillay), the École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne (Sandro Massidda), IBM of Kingston, New York (Giorgina Corongiu and Lorenzo Pisani), Cerfacs of Toulouse (Riccardo Scateni), the University of Konstanz (Bruno D’Aguanno),..Read More
First industrial research contract with a major company in the field of geophysical imaging
1993: signing of the first industrial research contract with a major company in the field of geophysical imaging for seismic prospecting. The activities, carried out by the Parallel Computing group, aim to introduce in the industrial context the technologies of concurrent computing through the implementation of a series of prototypes..Read More
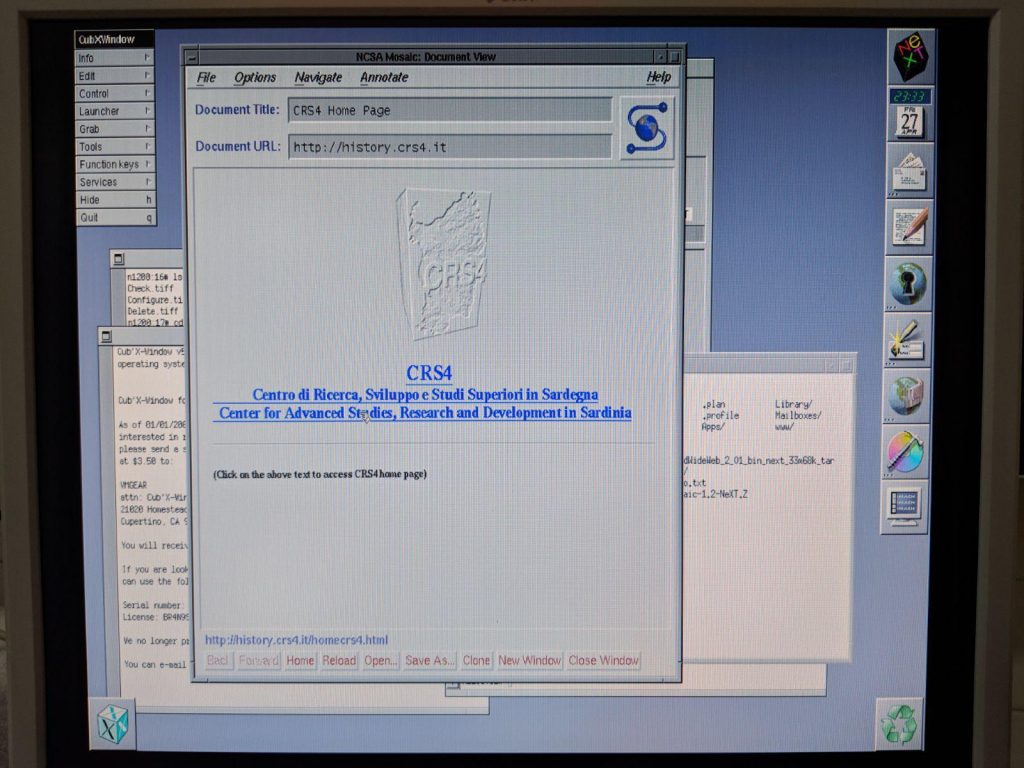
First italian website: crs4.it
August 1993: the first website in Italy is crs4.it In the early 1990s, only major universities and research centres had websites, mainly offering information about their structure and the local area. Search engines were still to come, so one had to browse through those websites to get generic information. Some..Read More
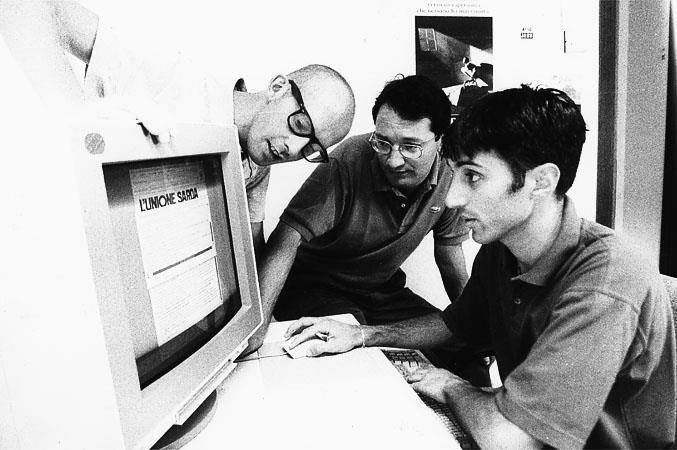
28 October 1993: "What about a WWW/Mosaic electronic version of L'Unione Sarda?"
With this fax begins the project that will lead to the online publication of the first European newspaper a few months later. Below is an excerpt from the book "Gazzette digitali. L'informazione locale sulla Rete globale", Andrea Bettini, ed.it, 2011 PZ: Everything was born out of a mixture of serendipity,..Read More
The first online newspaper in Italy is born: unionesarda.it
March 1994: CRS4 starts publishing the online edition of L’Unione Sarda, the first newspaper to go online in Italy and among the first in Europe. The idea came up from the collaboration between Pietro Zanarini, who headed the CRS4’s Scientific Visualization team, Reinier van Kleij, Systems Manager at L’Unione Sarda..Read More
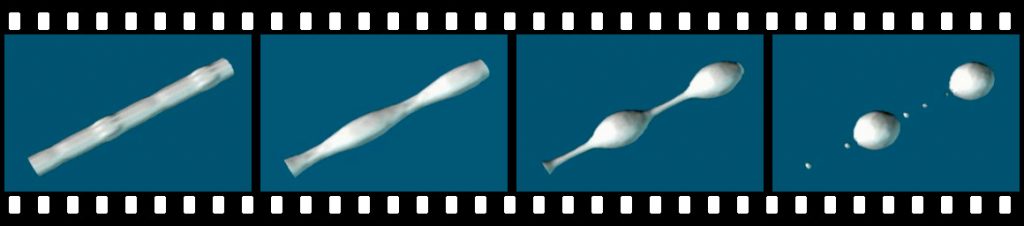
First 3D simulations of bi-phase fluids with merging and fragmentation
Researchers at CRS4, under the guidance of Gianluigi Zanetti, and in collaboration with Stéphane Zaleski (Pierre et Marie Curie University in Paris), develop new techniques for multiphase fluids based on Navier-Stokes equations, for example to simulate air and liquid fuel mixtures with explicit interface tracking. The work has had a..Read More
Liceo Alberti of Cagliari, first italian school online and the first in Europe with a Web server managed by students
In 1994 CRS4 with Gianluigi Zanetti proposed to some high schools in Cagliari to use the Internet at school. The Principal of the Liceo Scientifico Alberti, of Cagliari, the physicist Ugo Galassi, answers warmly and involves a young professor of physics, Roberto De Leo, who in turn enters the project..Read More
The first webmail born at CRS4
Luca Manunza, then a member of the CRS4’s Computational genomics group, headed by Gianluigi Zanetti, on February 20th, 1995 released publicly the code with which he created the first web-mail. The web-mail was not developed in the framework of the research project Manunza was working on, but thanks to the..Read More
Release of the first free VRML browser
CRS4 releases i3D, a system that combined for the first time the 3D input and high-performance rendering capabilities of high-end virtual reality systems with the data recovery capabilities of network browsers. Using a Spaceball, the user could intuitively navigate through three-dimensional data, while selecting 3D objects with the mouse activated..Read More
The first Italian search engine is developed at CRS4
CRS4 develops Search in Italy: the first Italian search engine dedicated to Italian web sites. Search in Italy, created by Gavino Paddeu (at the time in the SciViz group) contained an archive of 106,337 web pages that were periodically downloaded from the 660 Italian web servers existing at the time. The..Read More
Alfio Quarteroni appointed as Scientific director of CRS4
In 1995 CRS4 appointed Alfio Quarteroni, mathematician, former researcher at the CNR Institute of Numerical Analysis in Pavia, professor of Numerical Analysis at the Catholic University of Brescia and professor of mathematics at the University of Minneapolis (Minnesota), as Scientific Director. In previous years Quarteroni has had the merit of..Read More
THE TRISEE PROJECT AND THE BEGINNING OF THE SPECTRAL METHOD
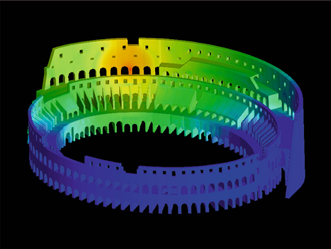
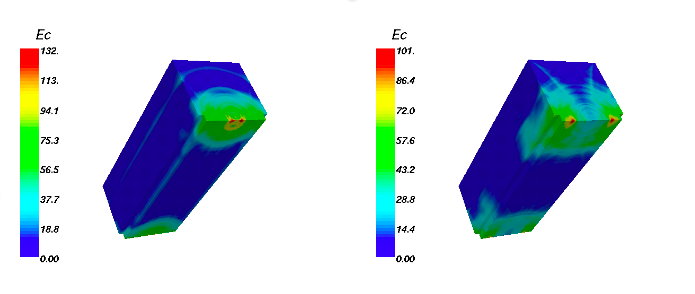
With the European Project Trisee the CRS4, along with Italian and European partners, promotes an innovative activity aimed to simulate the soil-structure interaction effects in the presence of earthquakes and man-made vibrations. These large-scale computational problems require a double effort, both for the development of optimized numerical algorithms and the..Read More
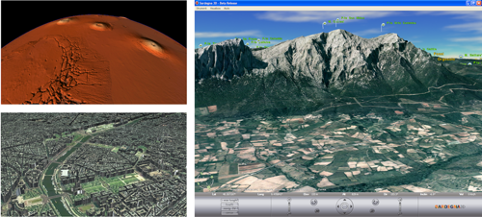
The Virtual Sardinia project at WWW '96
Enrico Gobbetti and Andrea Leone present Virtual Sardinia at the fifth International World-Wide Web Conference (WWW '96, Paris). The Virtual Sardinia project aims at collecting a large amount of heterogeneous data concerning the island of Sardinia and representing them in such a way that a casual user can easily navigate..Read More
The Energy Amplifier Project
In 1997 Carlo Rubbia involved CRS4 in the Energy Amplifier Project (also called Rubbiatron): a subcritical fast nuclear reactor (Accelator Driven System) coupled to a particle accelerator and cooled with liquid lead, able to use as fuel the radioactive waste produced by traditional nuclear reactors, together with thorium, a widely..Read More
CRS4 assigns Professor Marco Rosa-Clot as Scientific Director of the Research Division
In 1998 the CRS4 assigns Professor Marco Rosa-Clot the role of Scientific Director of the Rearch Division Professor Rosa-Clot Marco has accomplished his studies in Scuola Normale with 110/110 et laude in 1966. After one year of fellowship as researcher at Columbia University (New York 1968) he became charged Prof...Read More
Carlo Rubbia involves CRS4 in the Project 242: a nuclear propulsion engine
1998: Carlo Rubbia involves CRS4 in the Project 242: a study for a nuclear propulsion engine using Americium 242 for deep space travel. CRS4 took part in the preliminary design and sizing of the propulsion system, performing fluid-dynamic simulations and the simulations of the emission of nuclear fuel fission fragments,..Read More
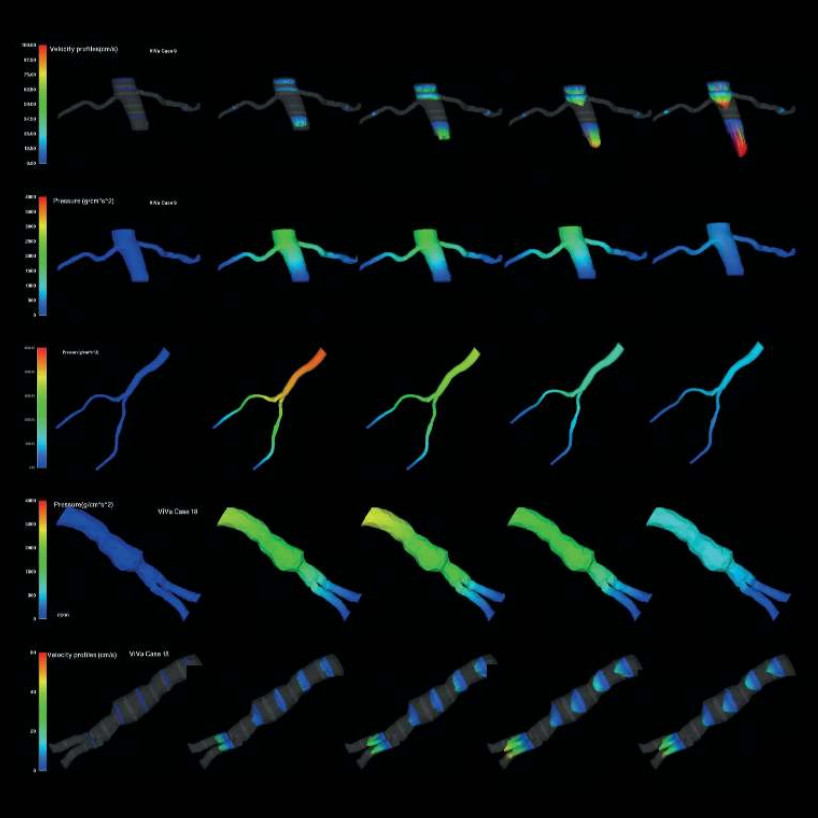
First personalized medical simulations of blood flow
Since its foundation, CRS4 has been at the forefront of research in data-intensive approaches aimed at creating specific and customized simulations based on the anatomical and physiological characteristics of an individual patient, in order to support medical research and clinical practice. In 1999, CRS4 was one of the first centers..Read More
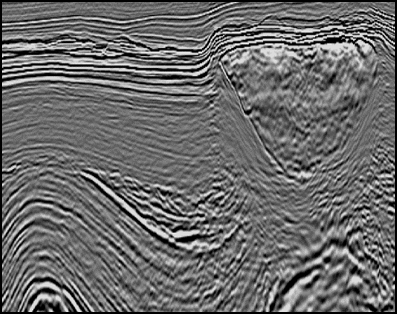
An innovative 3D pre-stack depth migration software overcomes the competition of commercial products
1999: within the second industrial research contract for geophysical imaging, the Parallel Computing group realizes a 3D depth migration application in the frequency domain so efficient it is transferred from the industrial partner's R&D department to the production one, overcoming the competition of commercial products. This result lays the foundation..Read More
CRS4 starts collaboration with Fiat Research Centre on the design of Fuel Cells
CRS4 starts the collaboration with the Fiat Research Center for the design of Fuel Cells for the power supply of electric cars. Thanks to the results achieved, CRS4 has become the reference center for modeling at national level in this field and continued in the years following, with the participation in..Read More
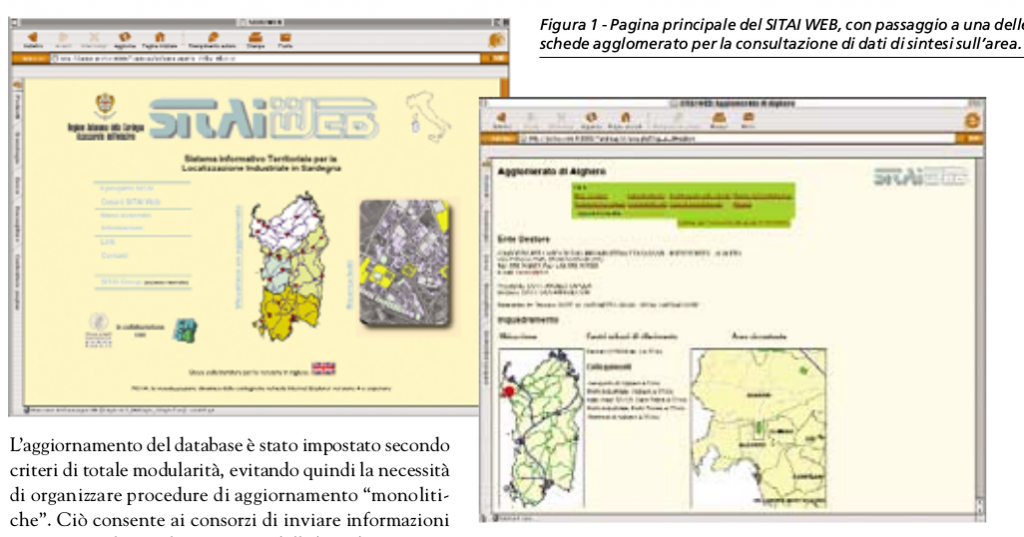
CRS4 develops one of the first multilingual GIS web systems in Italy
CRS4 develops one of the first multilingual GIS (Geographic Information System) web systems in Italy: SITAI (a GIS for the industrial areas of Sardinia), one of the first multilingual Web GIS in Italy. The system was developed by Eva Lorrai and Andrea Giacomelli using data from the Industrial Observatory of..Read More
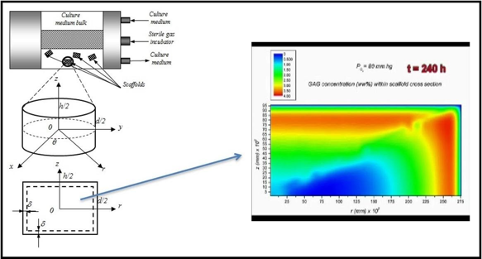
Mathematical models and computer simulation of cell growth and proliferation
In the early 2000s, following pioneering work carried out by an MIT research group in the emerging field of tissue engineering, CRS4 researchers began to develop mathematical models and computational codes for the simulation of engineered cartilage growth produced in a rotating bioreactor developed by NASA. The engineered tissue, to..Read More
Design of experiments on board the International Space Station
2002 In the framework of the Topical Team sponsored by the European Space Agency and coordinated by Giacomo Cao, at that time responsible of the Chemical Processes and Materials group at CRS4, the latter one has given a significant contribution, together with the researcher Massimo Pisu, to the design of..Read More
The "CRS-3D" software wins the prestigious "Eni Technology Award"
The "CRS-3D" software wins the prestigious "Eni Technology Award". The application, developed by the "Imaging and Numerical Geophysics" group of CRS4 for the reconstruction and regularization of seismic data based on the geometric modeling of the emerging wavefront, is still referred to by the specialists of the sector as an..Read More
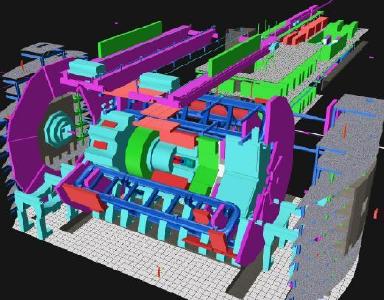
Simulations for CERN
CRS4 begins a collaboration with CERN for the design analysis of the Large Hadron Collider (LHC). The latter, the world's largest and most powerful particle accelerator, will run for the firs time in 2008. CRS4 carries out a number of numerical simulations with the aim of verifying the structural integrity..Read More
Introduction of novel methods for the scalable visualization of geospatial data
CRS4 made a significant contribution to the advancement of geospatial data visualization techniques by introducing a number of state-of-the-art models and GPU-accelerated methods in the early 2000s. These models and methods have been very well received by the scientific community and have led to numerous follow-ups. The open-source software for..Read More
CRS4 file the patent for a Solar Pond
On 15 January 2004, CRS4 filed the patent "Apparatus and method for heat extraction through a solar pond" later published on 16 July 2004, authored by Nicola Cabibbo, Erminia Leonardi, Luca Maciocco and Marco Rosa-Clot. Under the proposed extraction method, the deep layer of the Solar Pond flows slowly while..Read More
First Linux clusters
First medium-sized clusters based on 64-bit Linux, which had already been tested in 2000 thanx to a Gianluigi Zanetti's and the practical realization Alan Louis Scheinine (a former CRS4's whom after he left the center he worked at Louisiana State Universit, then Lockheed Martin and now retired) initially with 4 computers...Read More
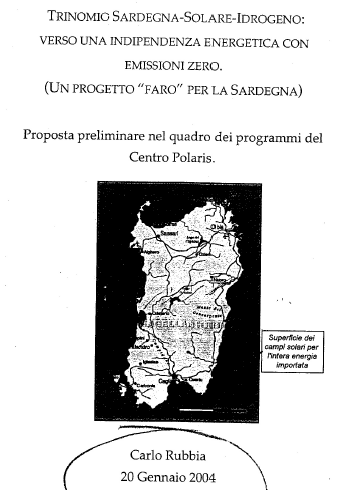
Project Trinomial: Sardinia-Solar Power-Hydrogen
In 2004 Carlo Rubbia presents to the President of the Regional Council, Mauro Pili, the "Trinomial Project: Sardinia-Solar Power-Hydrogen", which aims to produce hydrogen from renewable source (Concentrating Solar power). This was accompanied by a "Proposal for a feasibility study to make Sardinia energy and water independent" by designing thermal..Read More
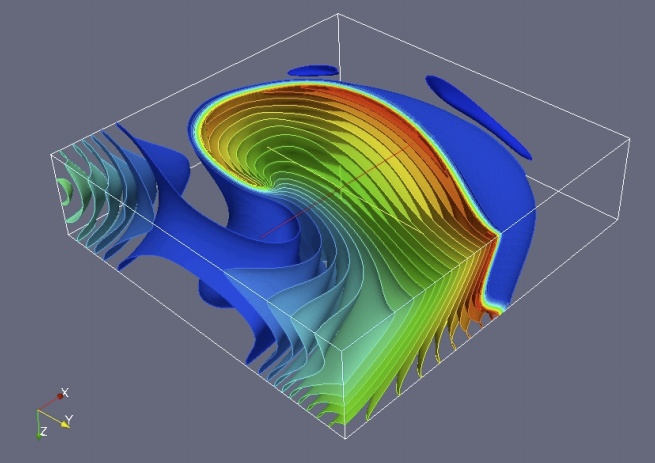
Introduction of the first scalable methods for viewing massive and complex 3D surface models
The interactive exploration of massive surface models generated by acquisition, simulation, or modeling has always been an extremely challenging task. In the early 2000s, CRS4 was among the first groups to take full advantage of the power of newly developed GPUs to offer effective solutions. In this context, one of..Read More
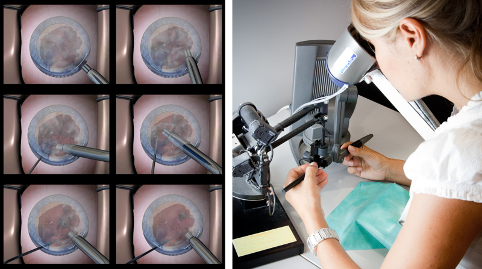
Real-time physical and visual simulations for eye surgery
Many of our visual computing technologies have been incorporated over the years into real-time simulators for various purposes. In 2005, a cataract surgery simulator with visual and tactile feedback was developed for surgical training. The simulator has been used in several training courses in Italy. The images shows a cataract..Read More
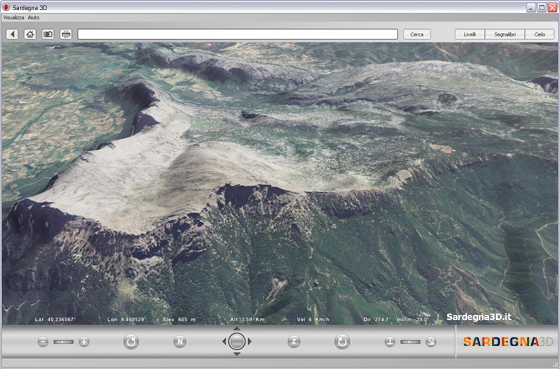
Sardegna3D
The Autonomous Region of Sardinia released the Internet geoviewer Sardegna3D, entirely based on the technologies developed in the Visual Computing sector for the scalable visualization of spatial data. The system made widely available for the first time very high resolution spatial data and thematic content. In the first two weeks..Read More
Mathematical models of microalgae growth in photobioreactors for CO2 capture and biomolecule production
In 2006, the CRS4, together with the University of Cagliari, started an intense research activity focused on the development of new cost-effective processes for the industrial scale exploitation of microalgae photosynthesis with the production of biofuels and simultaneous CO2 capture. More recently, the attention of the Center has focused on..Read More
Novel user interfaces and scalable visualization systems for the exploration of 3D models on light-field displays
CRS4 was among the first research centers to develop efficient visual computing methods and techniques to exploit the potential of new multi-projector light-field displays capable of creating virtual holograms in real-time. Meeting the performance constraints required by these systems is a challenging task, since they require the generation of hundreds..Read More
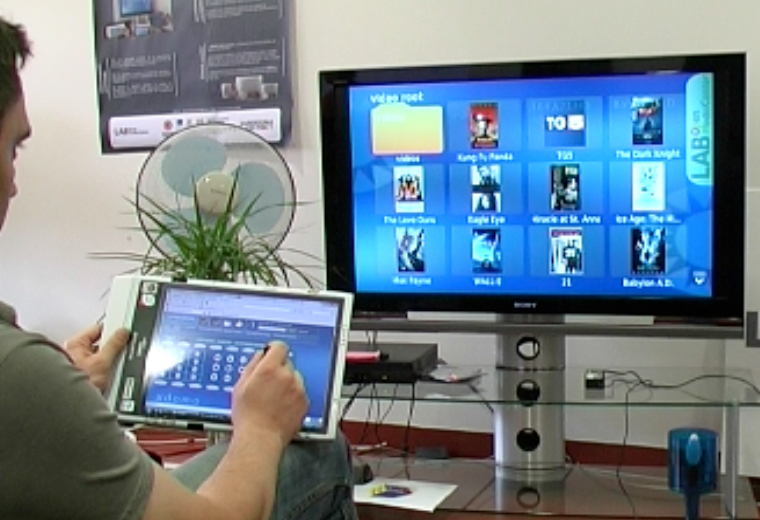
First experimental applications of SmartTV
Thanks to the wide capabilities of integration between different devices such as cell phones, PDAs, tablets and PCs, the potential of the network is exploited in order to find additional information. This information, associated in real time with the video content provided by the mediacenter, are displayed on the TV..Read More
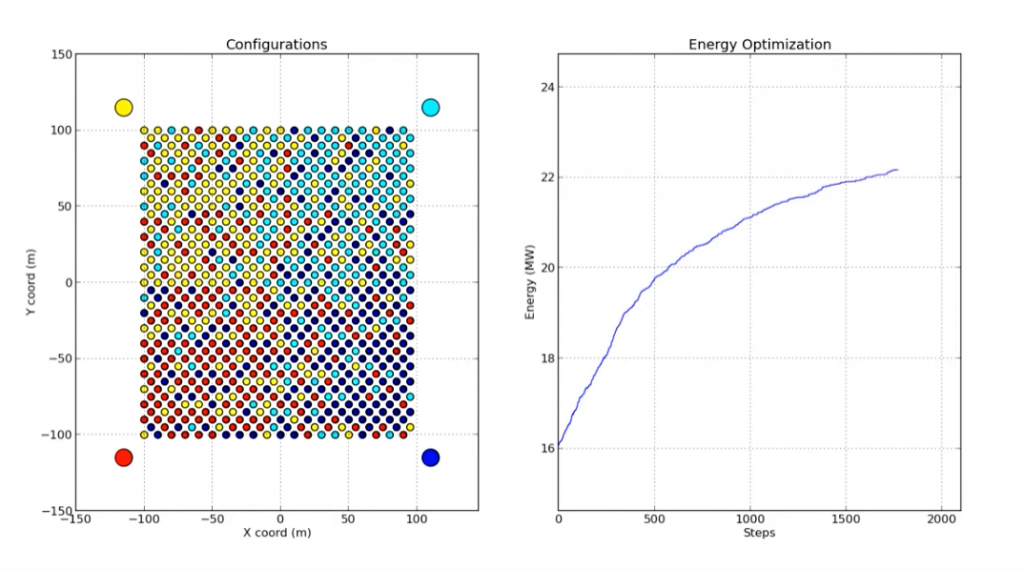
CRS4 enters the Top500 list of the most powerful High-Performance Computing systems in the world
2008 - After the expansion of its Computing Centre, the CRS4 enters, in 186th position, the Top500 list of the world’s 500 most powerful High Performance Computin centers. Its computing power and highly-skilled staff enable the CRS4 to work with the private sector, expanding the services of its computing platform..Read More
SIMULATION OF THE ELECTRICAL ACTIVITY OF THE HEART WITH HIGH ACCURACY SPECTRAL ELEMENTS
CRS4, in collaboration with the Oxford University and important industries like Fujitsu, Hofmann-Laroche, GSK, Novartis, takes part to the preDiCT project (EU FP7 ICT). Novel methods are dveloped for the simulation of the electrical activity of the heart in order to study in-silico side effects of drugs during the clinical..Read More
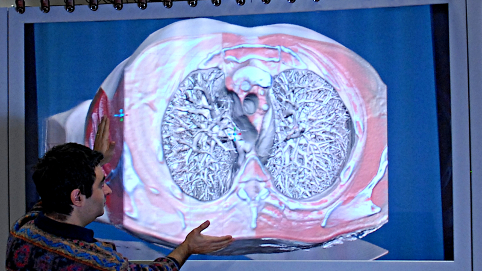
Introduction of the first scalable methods for transmitting and visualizing massive volumetric models
Over the years, CRS4 has developed a wide variety of methods capable of rendering potentially unlimited volumetric models on modern GPU platforms. These visual computing methods have found application in different fields, from medicine to science and engineering. After introducing in 2008 the first adaptive method capable of interactively displaying..Read More
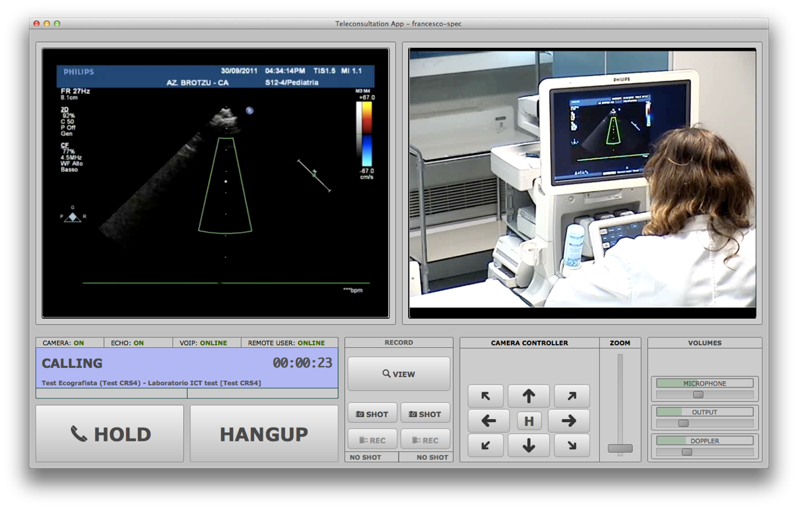
First trial of Paediatric Telecardiology
On 14 November 2008, a partnership between the Brotzu Hospital in Cagliari and CRS4 launched a real-time telemedicine project for congenital heart disease, through an innovative system based on low-cost open technologies, tested for the first time ever in Sardinia. The system enables the execution of an ultrasound scan with..Read More
Large multi-touch walls: CRS4's tFrame
CRS4's tFrame is a low-cost hardware/software architecture that enables multi-touch interaction on a generic display. Specifically, t-Frame is intended to be used in large size, multi-user interactive walls. With respect to other approaches tFrame can be installed as a pointing device on any flat surface regardless of size, shape and..Read More
Introduction of Pydoop - a simplified scalable platform for data analytics
Pydoop is an efficient and extremely simplified programming interface layer on top of Hadoop, while offering native compatibility with the full suite of Python tools for data science. Thanks to its flexible and efficient implementation, Pydoop proved to be an enabling technology for many other data-intensive activities. It formed the..Read More
New global non-linear minimization algorithm for the simultaneous optimization of 3D wavefront attributes
At the "79th Annual Meeting and International Exposition of the Society of Exploration Geophysics" in Houston, the "Imaging and Numerical Geophysics" group of CRS4 presents the algorithm for the simultaneous optimization of all geometric attributes of paraxial wavefronts reflected by deep subsurface discontinuities, an absolute novelty for both the world..Read More
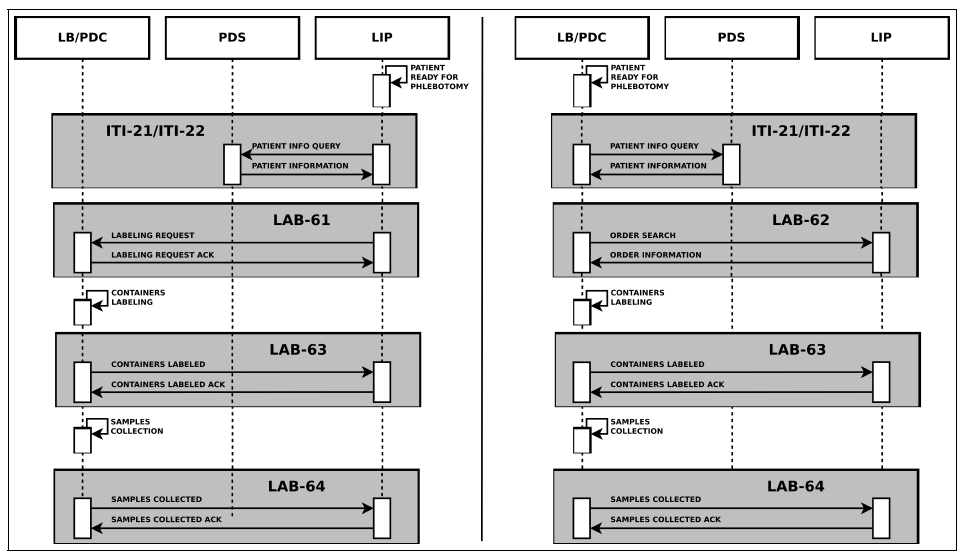
First contributions to international guidelines for clinical data and processes
Since the early 2000s, CRS4 has dedicated considerable efforts to data and process modeling through open formalisms, to technical and semantic interoperability among clinical domains, and to the creation of scalable systems for collaborative analysis and reuse of available information. In the health sector, CRS4 joined in 2010 the Technical..Read More
Development of processes for space exploration
In the framework of the COSMIC project sponsored by the Italian Space Agency and coordinated by Giacomo Cao, at that time responsible of the Bioengineering program at CRS4, the latter one has given a significant contribution, together with the researchers Massimo Pisu and Alessandro Concas, to develop novel processes and..Read More
CRS4 hosts the Eurographics international conference in Cagliari
In 2012, the European Association for Computer Graphics entrusts CRS4 with the organization of the 33rd edition of the Eurographics annual international conference, Europe's leading scientific event in the field of Computer Graphics. The conference, held in Cagliari from 14 to 18 May, was attended by over 400 researchers from all over..Read More
Open source tools for the management of biomedical data
CRS4 has focused for a long time on activities that aim to respond to the data management challenges generated by high throughput acquisition systems with continuously increasing sample size and data volumes. Among the first results of this line of activity is the collaboration with the Open Microscopy Environment (OME)..Read More
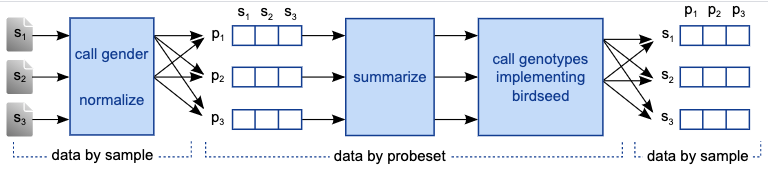
Scalable genomics data processing
CRS4 was a pioneer in the use of the MapReduce programming paradigm for the scalable processing of sequencing data. Among its various contributions in this context, CRS4 produced one of the early programs that used this paradigm to compute the DNA sequence mapping and identify duplicate sequences due to the..Read More
Molecular modeling of biological systems for medical and pharmaceutical applications: molecular modeling of the onset of autoimmune diseases
CRS4 has provided a significant contribution to the understanding of the potential mechanisms of onset and evolution of multiple sclerosis (MS), which are based on the interaction between specific environmental agents and cells of the immune system. The results of the models developed by CRS4, analyzed in collaboration with Sardinian..Read More
Filing of a patent for Solar Power Towers
On 5 February 2013, CRS4 filed a national patent application for a "Procedure and device for the control of a concentrating solar power system with several towers with heliostats", later published on 7 August 2014, authored by Marco Cogoni and Erminia Leonardi. The aim of the invention is to improve..Read More
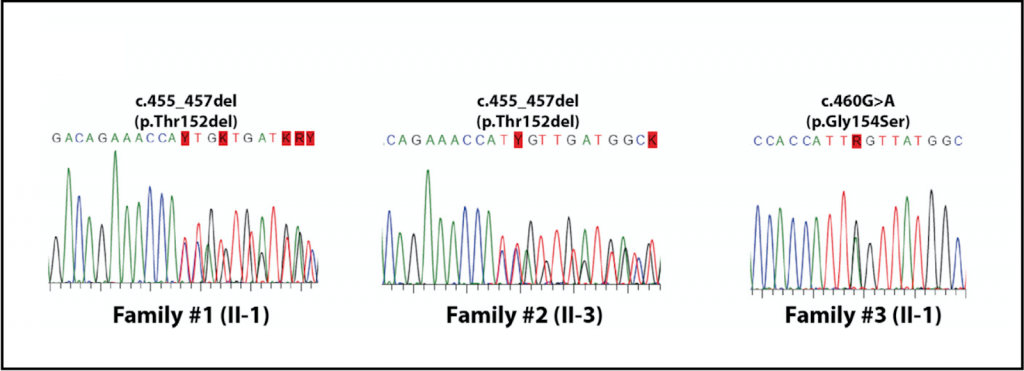
CRS4's sequencing platform significant contributions to important studies on population genetics
CRS4's sequencing platform provides a significant contribution to the successful execution of the study published on Science Magazine entitled "Low-pass DNA sequencing of 1200 Sardinians reconstructs European Y-chromosome phylogeny" (among the authors: Rossano Atzeni, Riccardo Berutti, Chris Jones, Frederic Reinier, Ilenia Zara) due of its expertise and facilities. Then in 2015 a new result..Read More
Digital Mont’e Prama
The Digital Mont'e Prama project aims to document, archive and present to the public the large and unique collection of prehistoric statues of the Mont'e Prama complex. Leveraging synergies with several other international research activities, the CRS4 Visual Computing group has studied, developed and applied new technologies for the complete..Read More
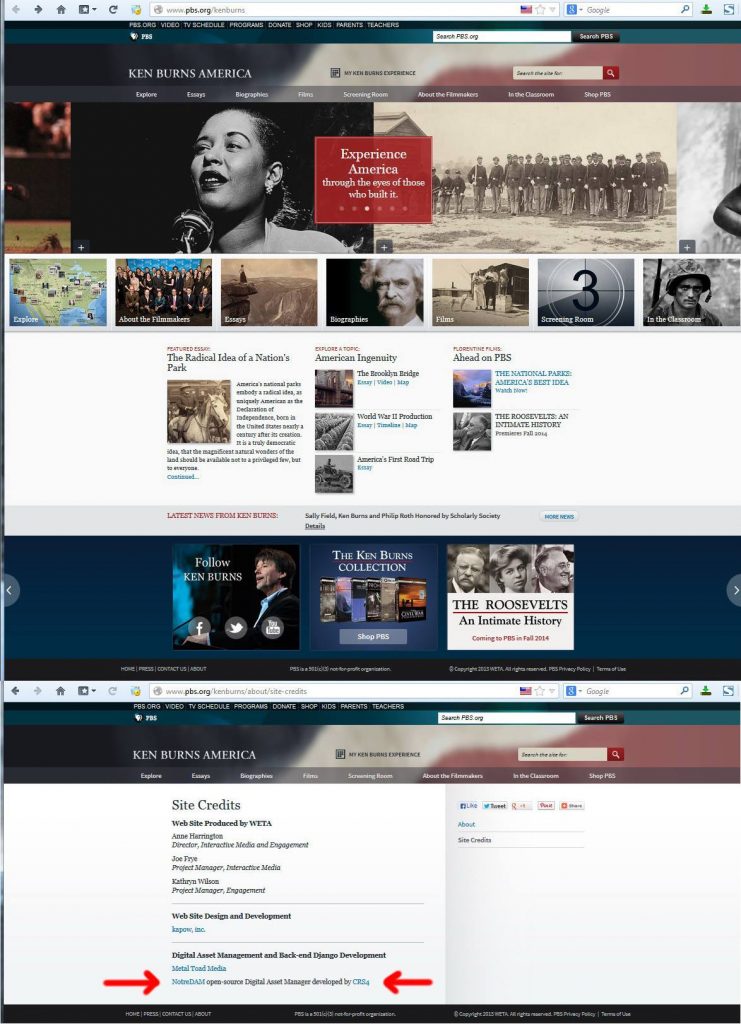
PBS's Kern Burns America project is powered by CRS4's NotreDAM Digital Asset Manager
The open source platform NotreDAM, developed by CRS4 with the contribution of Sardegna Ricerche, has been adopted as the digital library of Ken Burns America, a project promoted by US Public Broadcasting Service and aimed at providing access to the vast thematic digital content related to productions of Ken Burns,..Read More
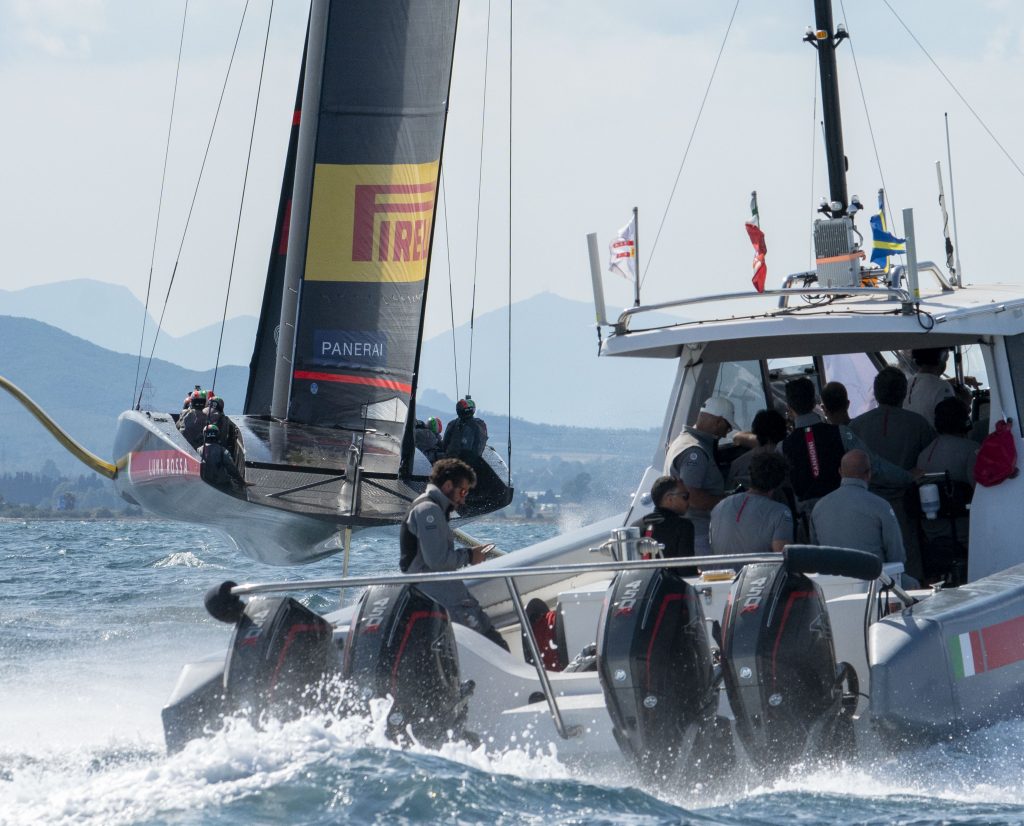
Collaboration with Luna Rossa Prada Pirelli begins
CRS4 starts scientific and technological collaboration with the Luna Rossa Prada Pirelli sailing team, which will last until 2020. CRS4 contributed its expertise in high-performance computing, innovative broadband networks for geographical area connectivity, sensor technology and radio infrastructure for data transmission for real-time boat monitoring during sailing races.
CRS4 hosts the EuroVis international conference in Cagliari
In 2015, the European Association for Computer Graphics and the IEEE Visualization and Graphics Technical Committee entrust CRS4 with the organization of the 17th edition of the EuroVis international annual conference, the leading European event in the field of Scientific and Information Visualization. The conference, held in Cagliari from 25..Read More
Large scale sequencing and analysis of genomic data
CRS4 has been a pioneer in the development of enabling technologies for the interpretation of data generated by NGS sequencing instrumentation and their use to identify the genetic variants underlying certain diseases. As an example of this activity, the image (taken from: A. Masotti, P. Uva, et al Keppen-Lubinsky Syndrome..Read More
Relevant contribution of CRS4 to a study published on Nature Genetics
CRS4 provides a significant contribution to the successful execution of the genetic study published on Nature Genetics with the title "Genome-wide association analyses based on whole-genome sequencing in Sardinia provide insights into regulation of hemoglobin levels" (international research collaboration led by Francesco Cucca) due of its computing expertise and computer center..Read More
Starts collaboration with Regional Department of Education
CRS4 (Education Technologies) starts a partnership with the Regional Department of Education, which continues to this day, through the project Tutti a iscol@. In the first year of the project, CRS4 helped to plan and deliver a program of extracurricular technology workshops for the schools of Sardinia. In all, more..Read More
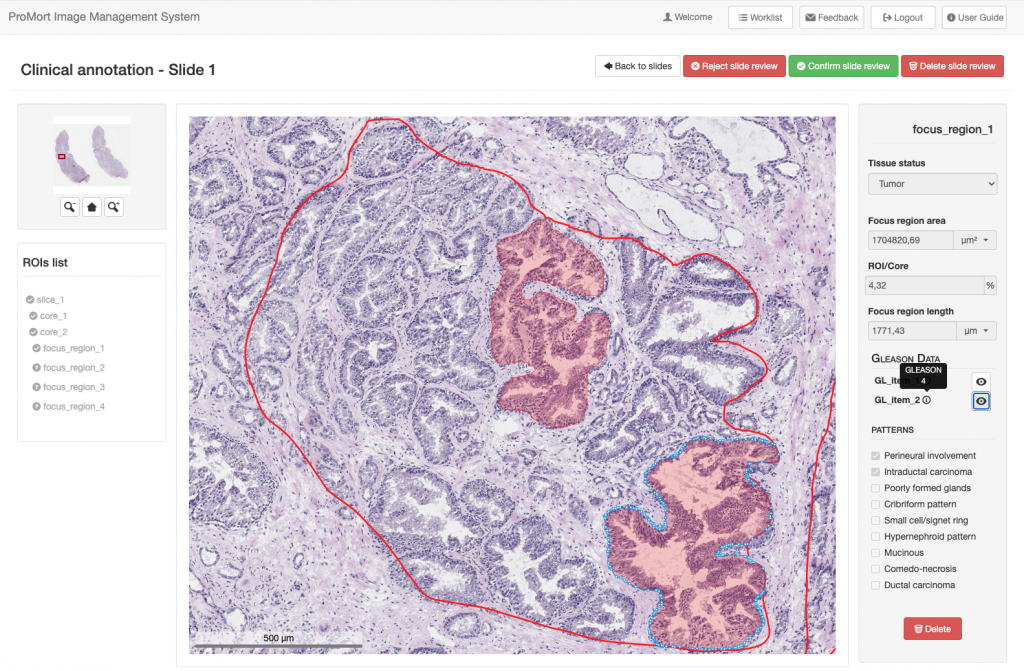
Advanced research platforms for the management of biomedical data
CRS4 addresses the challenge of managing large and complex biomedical data by creating and integrating open source tools to build research platforms for supporting the entire data transformation process - from raw data to primary analysis results. A significant example of this is the evolution of the CRS4 digital pathology..Read More
CRS4 hosts the largest Next Generation Sequencing platform in Italy
CRS4's Next Generation Sequencing Core Facility reaches in 2016 a throughput of 10 TBase/month, becoming the largest in Italy, with 1 x Illumina HiSeq3000, 1 x Illumina HiSeq2500, 2 x Illumina HiSeq2000 and 1 x Illumina MiSeq. The platform is directly connected to the CRS4 large scale computational resources. This infrastructure,..Read More
Automated deployment of platforms and programmatic management of infrastructures
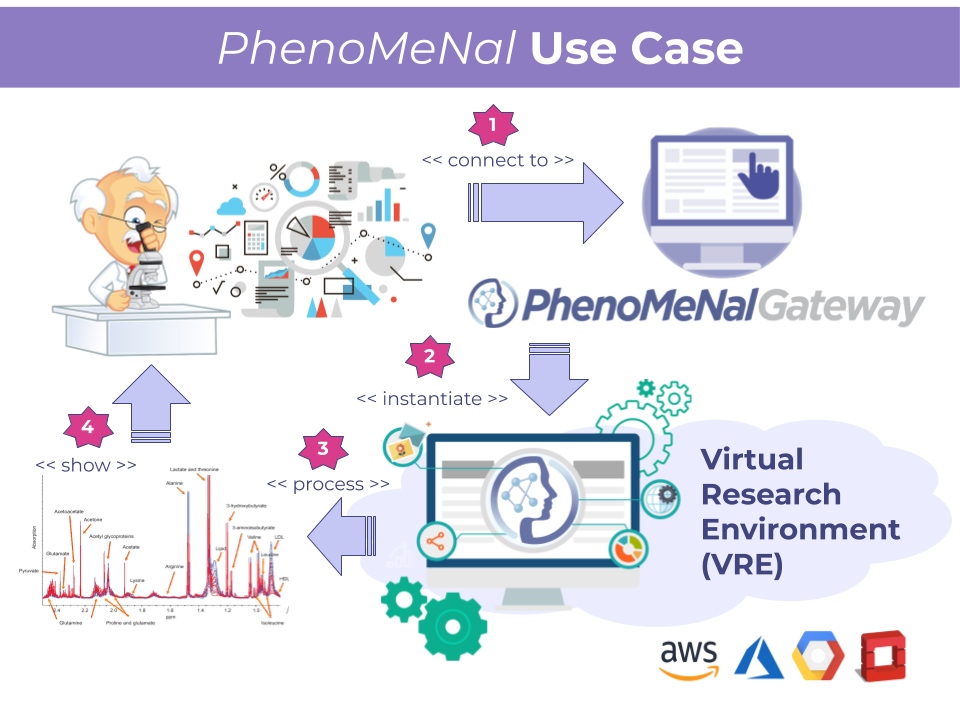
Since the technology first appeared, data-intensive computing researchers at CRS4 have been exploring the potential impacts of infrastructure automation and programmability on its activities. As an example, in 2016 CRS4 contributed to the creation of the PhenoMeNal e-infrastructure for scalable metabolomics data analysis, which can be trivially deployed and torn..Read More
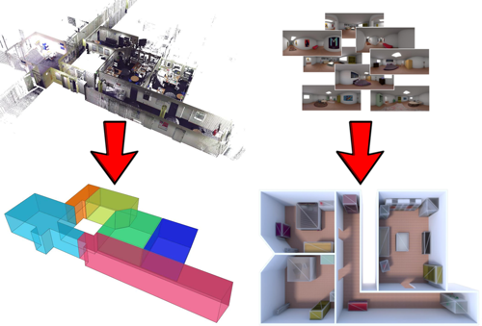
Automatic reconstruction of structured three-dimensional models
The automatic reconstruction of three-dimensional models from acquired data, whether images or 3D point clouds, has been one of the central themes of computer graphics and computer vision for several decades. In this field, CRS4 has introduced various cutting-edge visual computing technologies, using both geometric reasoning and deep learning approaches..Read More
CRS4 partners up with the Renewable Energy Platform
CRS4 joins forces with the Renewable Energy Platform, a department of regional agency Sardegna Ricerche. The aim is to transform CO2 from a problem into a resource. A new avenue of research is opened, on new CCU - carbon capture and use - technologies. The aim is to develop technologies..Read More
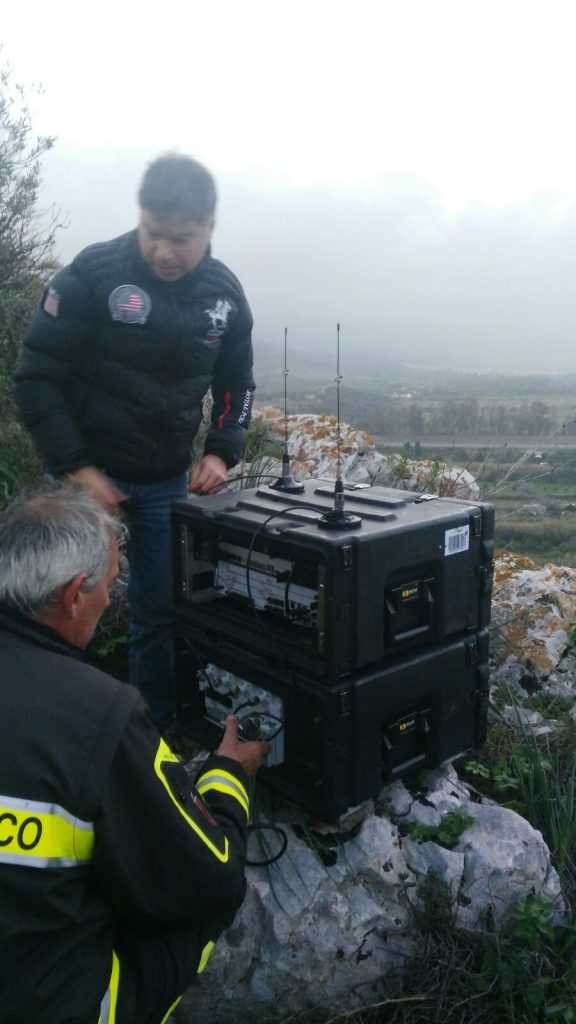
CRS4 participates in the mission to rescue the victims of the Rigopiano disaster
2017 - The portable system "Rapid e-LTE emergency solution", provided to the National Fire Brigade by the Joint Innovation Center under the collaboration between Huawei and CRS4, is used in the rescue operations at Rigopiano to transmit voice and data, including images, in an attempt to identify survivors. The system captures..Read More
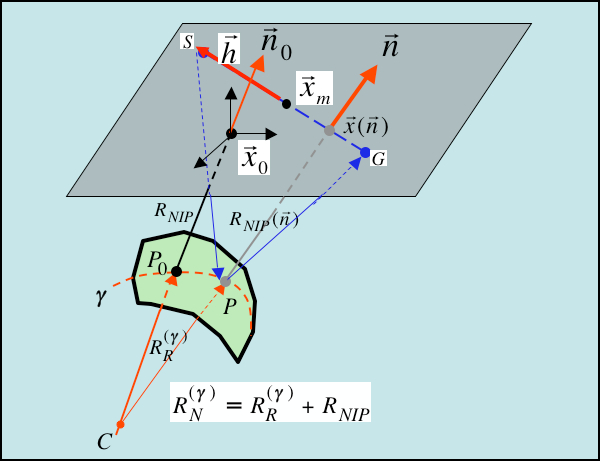
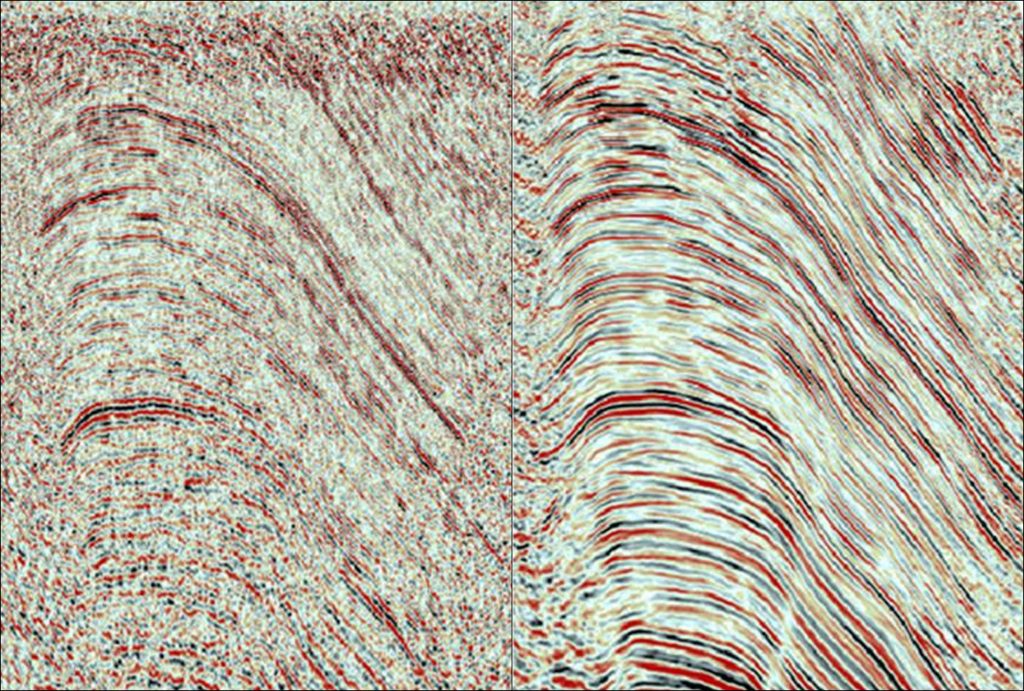
Innovative method of 3D time imaging, independent from the subsurface acoustic velocity
2017: the Journal of Geophysics and Engineering publishes the article "CRS theory based on a data-driven homeomorphism" in which the CRS4 group Imaging and Numerical Geophysics formalizes a new interpretation of CRS theory that leads to an innovative method of 3D time imaging, independent from the subsurface acoustic velocity and constructed in..Read More
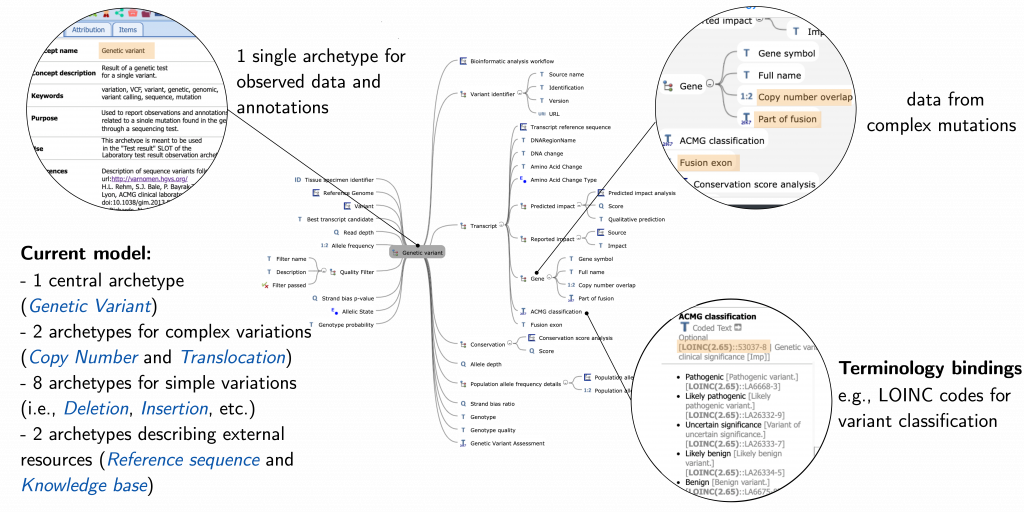
First genomic data models structured according to the openEHR formalism
CRS4 researchers have created the first models of genomic information through the openEHR formalism, leading an international collaboration with other research groups. openEHR is an international consortium that for over 15 years, through the issuance of technical specifications, data models and software, provides standardized tools for the semantic and computable..Read More
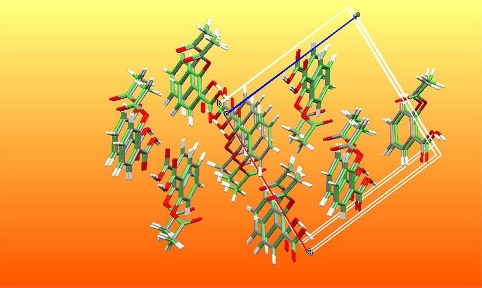
Data mining for the prediction of the physical-chemical properties of crystals
CRS4 has provided a significant contribution to the advancement of the state of the art in the field of prediction of physico-chemical properties and crystal structures by means of data mining tools. In particular, in 2018 it was demonstrated that a force field derived from the analysis of available experimental..Read More
Introduction of the first scalable methods for the transmission and visualization of massive time-variant volumetric models
After introducing in 2008 the first adaptive method capable of interactively visualizing static volumes of potentially unlimited size, CRS4 Visual Computing researchers made further progress by introducing various state-of-the-art compression methods (2012), in particular using sparse coding and tensor decomposition. In 2019, a further evolution of these methods led to..Read More
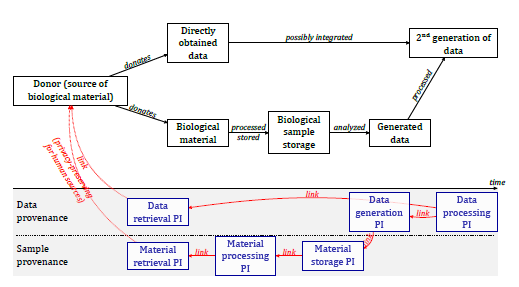
Approval of the ISO Committee for the first part of the standard on the provenance of data and samples in the biotechnology domain
The exchange of data and samples in clinical practice and biomedical research is increasingly common and necessary, but requires an effective evaluation of data and samples quality, which affects the reliability and reproducibility of the results obtained from their analysis. In this context CRS4 collaborates with BBMRI-ERIC (the European Biobank..Read More
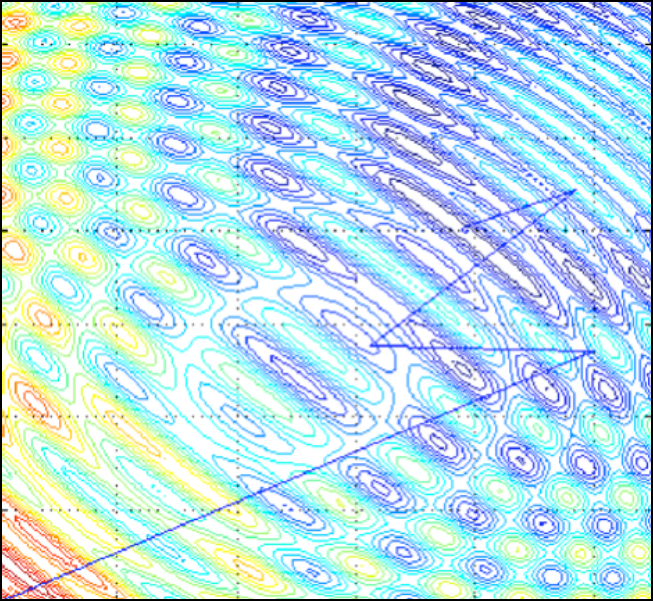
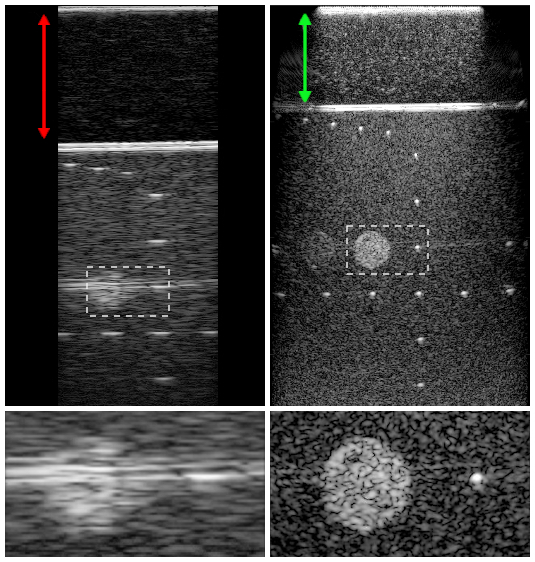
Application of an undulatory method of reflection seismics to the biomedical field
September 2020: Physical Review Applied publishes the article "Seismic Imaging Method for Medical Ultrasound Systems" where the CRS4 Imaging and Numerical Geophysics group successfully validates the idea of applying an undulatory method of reflection seismics to the biomedical field. The new algorithm considerably improves the resolution of ultrasound images, thanks..Read More
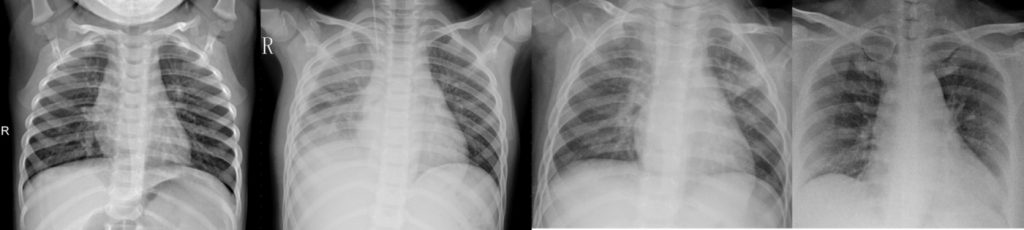
Classification of lung X-rays using AI: DIMASDIA-COVID19 project
In 2020 CRS4 participated in the DIMASDIA-COVID19 project. One of the activities aimed at diagnosing COVID19 by means of lung X-ray analysis. Deep learning AI was able to classify lung X-rays with a good degree of accuracy, distinguishing between bacterial, non-Covid and Covid viral pneumonia. The research was conducted by..Read More