CRS4 has provided a significant contribution to the understanding of the potential mechanisms of onset and evolution of multiple sclerosis (MS), which are based on the interaction between specific environmental agents and cells of the immune system.
The results of the models developed by CRS4, analyzed in collaboration with Sardinian hospitals, have been useful to guide clinical research and therapeutic approaches.
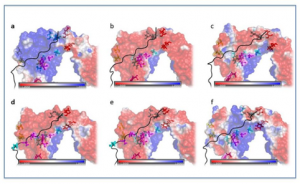
The image illustrates the results of the modeling of the electrostatic surface and amino acids involved in peptide binding for the 6 variants of the DQ protein present in Sardinian haplotypes recognized as predisposing (a, b, c, d) or protective (e, f) with respect to MS.